A lump on your jawline can be unsettling. While some are harmless, others may signal salivary gland cancer, a rare but serious condition.
Dr. Devendra Chaukar, a renowned head and neck oncologist in Mumbai, India, emphasizes the importance of early detection:
“Many patients ignore a persistent swelling on the jawline, assuming it’s a minor infection. However, if the lump persists or grows, it’s essential to get it evaluated by a specialist. The sooner we diagnose salivary gland cancer, the better the treatment outcomes.”
Ignoring the signs can delay crucial treatment. Let’s break down what this condition is, why it occurs, and how to recognize warning symptoms early.
Before we talk about cancer, let’s understand what these glands do.
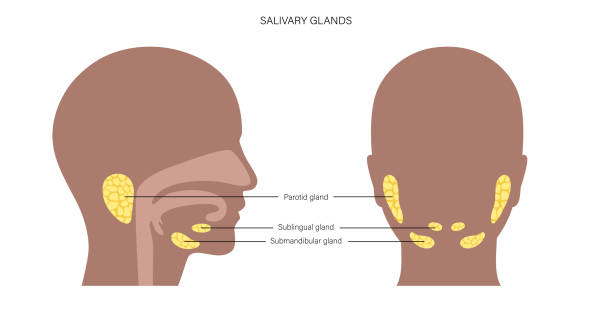
Salivary glands produce saliva, which helps in digestion, protects teeth, and keeps your mouth moist. You have three major pairs:
-
- Parotid glands – The largest, located near the jawline.
- Submandibular glands – Found under the lower jaw.
- Sublingual glands – Located under the tongue.
Tumors can develop in any of these glands, but most often in the parotid gland.
So, what could be behind that lump? Let’s delve into it.
What Causes a Lump on the Jawline?
A lump on the jawline can have several causes, ranging from harmless to serious:
Benign tumors – Non-cancerous growths like pleomorphic adenomas are common.
Salivary gland infections – Bacterial or viral infections can cause swelling.
Salivary stones (Sialolithiasis) – Blocked salivary ducts may lead to painful lumps.
Lymph node swelling – Often a response to infections or immune reactions.
Malignant tumors – A salivary gland cancer lump on jawline could indicate an aggressive tumor needing urgent attention.
Metastatic cancer – Cancer from another area may spread to the salivary glands.
Not all lumps are cancerous. But some warning signs shouldn’t be ignored.
How Can You Identify a Lump That Could Be Linked to Salivary Gland Cancer?

A cancerous lump has distinct characteristics:
-
- It feels firm or fixed and doesn’t move easily under the skin.
- It grows over time rather than shrinking.
- You may experience pain, numbness, or weakness in the jaw or face.
- There may be difficulty swallowing or a persistent dry mouth.
If you notice these salivary gland cancer symptoms, consult a specialist immediately.
Concerned about a lump on your jawline? Book an Appointment with a trusted head and neck oncologist for early diagnosis and treatment.
What Are the Risk Factors for Developing Salivary Gland Cancer?

Certain factors make you more likely to develop this cancer.
Age – More common in older adults.
Radiation exposure – Previous radiation therapy to the head or neck increases risk
Tobacco and alcohol use – Long-term use may contribute to head and neck cancers.
Genetic factors – Family history of salivary gland tumors.
Viral infections – Some viruses, like HPV, may increase the risk.
Workplace exposure – Jobs involving exposure to chemicals (e.g., rubber, asbestos).
Being aware of these risk factors can help with early detection and prevention.
How does this cancer impact survival and recovery? Read on to find out.
What Is the Prognosis for Someone with Salivary Gland Cancer?
The prognosis for salivary gland cancer depends on several factors, including the tumor type, stage, location, and how early it is diagnosed. Generally, earlier detection leads to better outcomes.
Key factors affecting prognosis:
Tumor type – Some subtypes, like adenoid cystic carcinoma, tend to grow slowly but can spread to nerves and lungs over time. Others, like mucoepidermoid carcinoma, can range from low to high aggressiveness.
Cancer stage – Early-stage cancers (Stage I & II) have a higher survival rate compared to advanced-stage cancers (Stage III & IV).
Tumor location – Cancers in the parotid gland often have a better prognosis than those in the submandibular or minor salivary glands.
Spread to lymph nodes – If the cancer has spread to lymph nodes or distant organs, treatment becomes more complex, lowering survival chances.
Response to treatment – Surgery combined with radiation therapy offers the best outcomes for most patients. Chemotherapy may be used in advanced cases.
Survival Rates
While survival rates vary, studies show:
-
- Stage I & II: 70–90% 5-year survival rate
- Stage III: Around 50–70% 5-year survival rate
- Stage IV: 25–50% 5-year survival rate
According to Dr. Chaukar, “Advancements in minimally invasive and robotic surgery have improved patient outcomes. Today, we focus not just on treating cancer but preserving function, ensuring that patients can continue speaking, eating, and living comfortably.”
How Can You Prevent Salivary Gland Cancer or Lumps on the Jawline?
While salivary gland cancer cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle choices may reduce the risk.
Avoid tobacco and alcohol – Smoking and heavy alcohol use increase the risk of head and neck cancers.
Protect yourself from radiation exposure – Excess radiation, including previous radiation therapy to the head and neck, may raise the risk.
Maintain good oral hygiene – Regular dental checkups and oral care can help detect abnormalities early.
Stay hydrated – Drinking plenty of water supports healthy salivary gland function and prevents blockages.
Eat a healthy diet – A diet rich in fruits and vegetables provides antioxidants that may help protect cells from damage.
Limit workplace chemical exposure – If you work around pesticides, nickel compounds, or silica dust, use protective gear to reduce exposure.
When to Consult the Doctor?
See a doctor if you notice:
-
- A lump that persists for more than two weeks
- A painless lump that is growing
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking
- Facial numbness or weakness
If a lump changes in size, shape, or causes discomfort, don’t ignore it. Early evaluation can make a difference.
Conclusion
A salivary gland cancer lump on jawline may not always be cancerous, but it should never be overlooked. Early detection and timely treatment improve outcomes significantly. If you notice a persistent or growing lump, consult a specialist like Dr. Devendra Chaukar, a leading head and neck oncologist surgeon in Mumbai.
Your health is in your hands. A simple checkup can prevent serious complications—never hesitate to get a lump evaluated.
FAQ
Is salivary gland cancer common?
It is rare but can be aggressive. The parotid gland is the most common site.
How is salivary gland cancer diagnosed?
Doctors use physical exams, imaging tests (MRI, CT scan), and biopsies to confirm if a lump is cancerous.
What is the best treatment for salivary gland cancer?
Treatment usually involves surgery, radiation therapy, and sometimes chemotherapy, depending on the stage and type of cancer.
Does salivary gland cancer spread quickly?
Some types grow slowly, while others spread rapidly. Early detection improves outcomes.
Can salivary gland cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Yes, in some cases, salivary gland cancer can spread (metastasize) to lymph nodes, lungs, or bones if not treated early.
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes only and not for promotional use.

Dr Devendra Chaukar
Dr. Devendra Chaukar is a renowned Head and Neck Surgical Oncologist with over 20 years of experience in treating complex head and neck cancers. A graduate of Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai, he specializes in minimally invasive surgeries and organ-preserving treatments. Dr. Chaukar is deeply committed to patient-centric care and advancing cancer treatment through research and education.


Recent Comments